
SAMS serves as the primary tool for reporting and tracking immunizations for Navy and Military Sealift Command fleet assets. SNAP (Shipboard Non-Tactical ADP Program) Automated Medical System (SAMS) If you have difficulty accessing or using this system, contact ASIMS at (210) 395-9742. Air ForceĪeromedical Services Information Management System (ASIMS)ĪSIMS is a web-based application that provides the Air Force the capability to track medical readiness, including immunization data, through a web portal for all personnel both in fixed or deployed facilities. If you have difficulty accessing or using this system, contact MRRS at (800) 537-4617. MRRS gives headquarters staffs and leadership a real-time view of Force Medical Readiness and immunization status. MRRS is a web-based, real-time application with a central aggregating database, which links with existing authoritative data systems for personnel tracking including the Navy Standard Integrated Personnel System (NSIPS) and Marine Corps Total Force System (MCTFS).
MRRS is the Navy, Marine Corps and Coast Guard’s tool designed to record and track Individual Medical Readiness (IMR) elements to include immunizations, dental status, laboratory tests, and physical exams such as periodic health assessments, deployment health status, pregnancies, illnesses, and injuries. Medical Readiness Reporting System (MRRS) If you have difficulty accessing or using this system, contact MEDPROS at (877) 256-6477 or via email at Hours of operation: 0600-1800 EST Mon-Fri, 0700-1700 Sat-Sun. Post-Deployment Health Re-assessments (DD2900).MEDPROS also provides every Soldier with alerts as to their Individual Medical Readiness status.Īs an important part of the Medical Operational Data System (MODS), MEDPROS contains four key modules: The primary users of the MEDPROS online applications are the Soldier Readiness Processing (SRP) locations, Medical Treatment Facilities, National Guard State and Army Reserve RRC Surgeon's Offices, and unit Commanders at all levels who need to monitor the Medical Readiness status of their subordinate units and Soldiers. Rabies in the U.S.MEDPROS provides for the data entry and reporting/tracking of medical and dental readiness information for Soldiers, Units, and Task Forces.Programs for uninsured and underinsured patients.
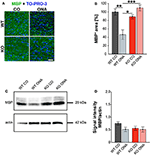
#Immunized 2199 im pro plus
What kind of animal did you come in contact with? plus icon.RIG is unnecessary and should not be administered to these persons because an anamnestic response will follow the administration of a booster regardless of the pre-booster antibody titer. Previously vaccinated persons are those who have received one of the recommended preexposure or postexposure regimens of HDCV, RVA, or PCECV, or those who received another vaccine and had a documented rabies antibody titer. If exposed to rabies, previously vaccinated persons should receive two IM doses (1.0 mL each) of vaccine, one immediately and one three days later. HDCV or PCECV 1.0 mL, IM (deltoid area), one each on days 0 and 3. Postexposure Prophylaxis for Previously Immunized Individuals Treatment * A 5th dose on day 28 may be recommended for immunocompromised persons. HDCV or PCECV 1.0 mL, IM (deltoid area ), one each on days 0, 3, 7, and 14. Because RIG might partially suppress active production of antibody, no more than the recommended dose should be given. Also, RIG should not be administered in the same syringe as vaccine.
#Immunized 2199 im pro full
If possible, the full dose should be infiltrated around any wound(s) and any remaining volume should be administered IM at an anatomical site distant from vaccine administration. If available, a virucidal agent such as povidine-iodine solution should be used to irrigate the wounds. Postexposure Prophylaxis for Non-immunized Individuals TreatmentĪll postexposure prophylaxis should begin with immediate thorough cleansing of all wounds with soap and water. The gluteal area should never be used for rabies vaccine injections because observations suggest administration in this area results in lower neutralizing antibody titers. For children, the anterolateral aspect of the thigh is also acceptable. For adults, the vaccination should always be administered intramuscularly in the deltoid area (arm). Additional doses should be administered on days 3, 7, and 14 after the first vaccination. When children do get the disease, they’ll likely have lifelong immunity. The first dose of the four-dose course should be administered as soon as possible after exposure. A regimen of four 1-mL doses of HDCV or PCEC vaccines should be administered intramuscularly to previously unvaccinated persons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
